Table of contents:
The advantages of breastfeeding
Feeding diet
Breastfeeding - how often?
How long should I breastfeed?
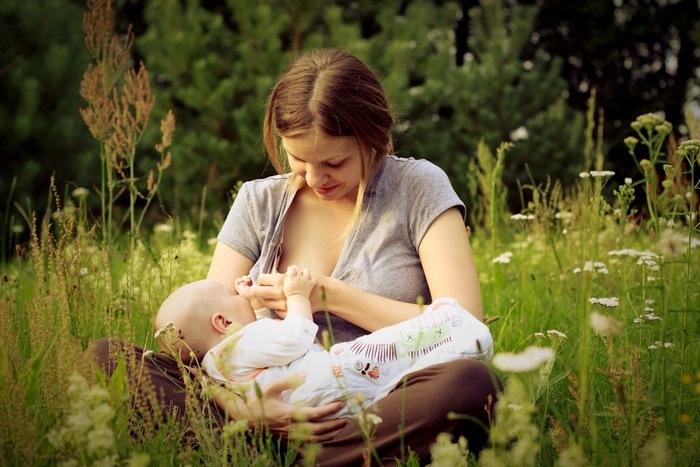
Breastfeeding positions
When to breastfeed?
Breastfeeding after a caesarean
Breastfeeding problems
Nursing a newborn - how to prepare?
Cigarette smoking and breastfeeding
Contraception and breastfeeding
Breastfeeding and beauty treatments
Breastfeeding during menstruation and pregnancy
What are the advantages of breastfeeding?
Each young mother asks if the advantages of breastfeeding outweigh the advantages of giving the baby artificial food from the first days after the birth. Therefore, let us briefly explain what are the most important benefits of breastfeeding and why it is worth choosing this form of nutrition for a baby.
Numerous advantages of breastfeeding arise primarily from the fact that it is a natural process that in humans, like all other mammals, allows the newborn baby to provide adequate nutrients and vitamins. The mother's milk also contains all the necessary antibodies and helps to develop immunity of the baby, so that in the future it will be less susceptible to viral and bacterial infections, as well as the negative effects of all other types of microorganisms. The food also contains natural pre- and probiotics, which also reduces the child's susceptibility to diarrhea caused by infections. In addition, thanks to a relatively long breastfeeding period, even longer than the first year of the child's life, we prevent allergies occurring in the future, as well as overweight and diabetes. In addition, the composition of the mother's food changes over time in such a way as to provide the child with appropriate nutrients depending on the time of day and the age of the baby. Milk changes even during each single feeding session - at the beginning, it contains more water, thanks to which it satisfies the child's thirst and then changes into a more nutritious food with a higher calorie content.
However, not only the youngest member of our family benefits from breastfeeding. Also for the mother, it is a process that helps with getting back to the pre-pregnancy form faster. First of all, during breastfeeding the so-called happiness hormone, ie oxytocin is released, which is not only the natural way of the body to improve the mood in this difficult and new situation for each mom. Oxytocin also makes the postpregnancy period much shorter than for women who do not breastfeed. In addition, for women who breastfeed, it is much easier to lose extra kilograms, which our body postpones during pregnancy just at the time of lactation, when stored stocks are used for the production of food by the body. During the breastfeeding period, we also tend to pay attention to our diet and avoid potentially unhealthy stimulants, which affects not only the child but also the health and well-being of each mother.
Let's also not forget that natural food is available anytime, anywhere. We do not have to get up at night to prepare a bottle with a properly prepared artificial mixture that can only be served at a certain temperature. We do not take extra milk powder packages with us on the trip, and we do not need an extra bottle for a walk or when going out with friends. It also involves large savings. Both artificial food and accessories needed for it, bottles, teats and other elements are a monthly cost from several dozens to even several hundred zlotys. If we have such a possibility, it is worth choosing to breastfeed your baby at least in the first few months of his life. This will have positive effects for both him and you, your figure and wallet.
Are there any special foods that we should eat while breastfeeding?
At the beginning of breastfeeding, we may wonder what to eat so that our food contains as many nutrients as possible for a newborn to develop. Are there any dishes that we should introduce to our menu? Or maybe it is necessary to avoid certain types of food?
At the beginning, it is worth noting that the popular diet of elimination, which has already a dozen or so years, has already been officially recognized as a serious mistake. Adequate nutrition of a young mother should not at all exclude foods that could potentially harm the child. A much better approach, currently recommended by specialists, is to pay attention to whether the child has a colic or other stomach discomfort after some dishes are eaten by the mother. Many of them even claim that the mother's diet does not have a direct impact on the digestive system of the child - substances that are responsible for bloating caused by eating cabbage or beans do not get into the milk. Nevertheless, thanks to careful observation we will be able to determine whether the baby is not allergic to cow's milk or its products, and what other substances consumed by us may make him allergic.
In addition, the habits that every nursing mother should apply, do not differ from those recommended by nutrition specialists to any other person. We should unconditionally give up highly processed food containing numerous dyes, preservatives and flavor enhancers, as well as foods that are hard to digest and contain relatively little nutritional value. The latter will primarily include mushrooms and fatty meats and fried meat. It is also necessary to also discontinue drinking sweetened soda and alcohol, which can get into the food and seriously harm the child. It is also worth giving up drinking large amounts of strong coffee, although a cup for breakfast will certainly help us to survive the difficult beginnings of motherhood rather than hurt the child. Our diet should also consist of a large number of complex carbohydrates, which can be found in wholegrain bread and groats and brown rice. In each meal should be vegetables and fruits, and every day we should eat at least a small amount of green and leguminous vegetables, nuts, eggs and lean meat. These products will provide us with the amount of iron necessary for the proper functioning of the body and prevent the occurrence of anemia. At least once a week, it is also worth to prepare oily sea fish for dinner, which contain beneficial omega-3 acids, as well as vitamin D. And once you get used to this diet during breastfeeding, it is worth staying with it also after finishing the process. It is the healthiest menu recommended by dieters, which will have a huge impact on your well-being and figure!
Breastfeeding - How often should you do it?
The fundamental question that arises in the mind of every young mother is this question - how often should I feed my baby? The answer is (except for a few special cases) simple and concrete: as often as it's hungry. Latching a baby to the breast on demand is the healthiest and most recommended method of breastfeeding. The baby's body perfectly specifies the point at which it needs another dose of food and the baby is able to signal it adequately - most often through excitement and restless behavior. It can also put hands to it's mouth and look around. If these hunger signals are ignored or the young mother does not recognize the cause, the baby begins to cry. Then the feeding process itself may be a bit more complex and definitely more difficult, so it is best to constantly watch your baby and be "on alert" in case of any signs of hunger. With time the feeding routine will stabilize and it will be possible to predict when the baby will wake up to look for your breast. In the first days of life, a newborn baby may demand a meal every hour or a half. Over time the frequency falls - the first weeks spent together are usually 8 to 12 days of breastfeeding. If your child wants to eat less than 8 times a day, you should additionally wake them up to latch to the breast. Night feeding is also very important - it helps to maintain normal lactation and meet the basic needs of a baby which is hungry not only during the day. With every week your baby's stomach is constantly growing, so it can hold more milk. That is why the baby is able to eat "in case" and the time between meals increases to 2-3 hours. After two months, the baby is able to sleep up to 6 hours without feeding interruptions, which guarantees some well deserved sleep for the mom.
How long should I breastfeed? How many minutes should it take to breastfeed?
The meal time is not only satisfying the baby's appetite but also building a sense of security. The more time a child spends in his mother's arms, the greater the bond between them. The first feeding should last as long as the baby needs it. They usually oscillate around 20 minutes during which the child slowly and successively feeds. Divide this time in half and latch it once to one breast, once to the other - they should be used evenly to avoid swelling and problems with further lactation. If your child falls asleep during a meal time, gently remove it from the breast and place it in the crib. You can not let your breast be treated like a teat. Over time the baby will find out that feeding and sleeping are two separate activities, which will save you time and help to more effectively fill your baby's tummy.
Breastfeeding positions. Discover the most convenient techniques for feeding your baby!
The position taken during breastfeeding is of great importance to the comfort and safety of your baby. The mum's comfort is also important - feeding should not manifest as muscle pain or fatigue. It is a special time that both of you should associate with the closeness and enjoyment of spending time together.
Main principles of breastfeeding:
- Keep the baby close to you - your nipple can not protrude, and the toddler should not force his head out
- Your baby's head should be at the height of your breast
- Remember to allow the child to breathe freely through the nose
- The toddler's head and spine should be in one straight line
- Make sure your child does not lean forward or backward
- If your baby wants to do it, it should be able to unlatch from the breast
- The baby's body should be closely attached to the mother's body
- To breastfeed more comfortably use the breastfeeding clothes
At different times of breastfeeding, women prefer a variety of ways to latch the toddler to the breast. Depending on your individual preferences, you can choose one of the recommended positions and modify it accordingly:
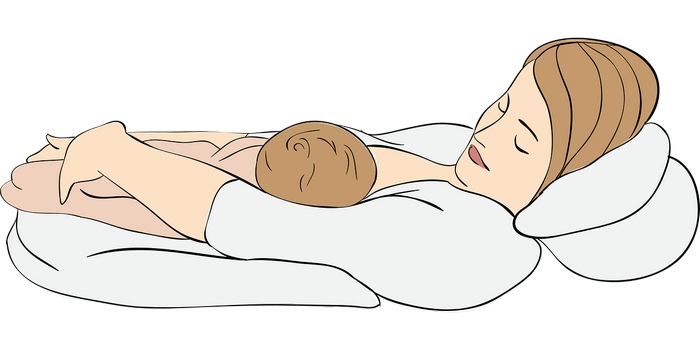
Position for feeding on the side
Sit comfortably on the side of the feeding breast. Put a pillow under your head and shoulders. If you need, add one more between your knees. This should improve the comfort of the feeding process.
Feeding on the side is especially recommended during the first feeding, when sitting down may cause some mothers a bit of difficulty. This position has also been recognized as a way of night feeding.
The baby's head should be slightly higher than the rest of the body, but still in the symmetry axis defined by its spine.
On the side you can also breastfeed with the opposite breast - just put your weight on the elbow and put the baby the other side of the body.
Feeding position on the back
Lie on your back and bring your baby to your belly. When the baby latches to the nipple, make sure that it can breathe freely. In this position it is important that the baby can freely reach the greater part of the breast than the nipple itself.
The back position is recommended for mothers who have had a c-section or noticed that the milk flows quite rapidly during the first minute of a child's meal.
Feeding position for sitting
Also known as the classical position. For comfort while feeding a child in a sitting position, a properly prepared seat is necessary. An armchair or chair can not be too low for the thighs shouldn't be too close to the chest. Seats too high, on the other hand, will cause the hips to slide towards the ground. It's a good idea to prepare some cushions for the baby in case you have to move the baby closer to your breast, they can support muscles of your hand or help you sit straight on the armchair.
There is also a variant of this position, where some moms choose to sit on the floor. In this position you sit down with your legs crossed, lean the toddler on your forearm and set it obliquely with your hand holding his hips. In this position the mom and the child should touch bellies.
Lower back position
Position similar to the classic, sitting technique - only the child supporting hand is switched. This means that we hold the baby with the forearm opposite to the breast that we feed it with. For example: while feeding the baby with your left breast, hold it with your right hand. Your bellies should come in contact, your hand should secure the neck and head of your toddler and your back should rest on your forearm.
This position is recommended for mothers of exceptionally vigorous children who tend to have headaches or have problems with proper suction as it allows for very precise latching.
The armpit position (also called the football position)
One of the positions recommended for premature babies and children who have grown accustomed to one particular breast is the position that makes you put the toddler under the arm. Your hand holds the head and neck of the toddler, his belly is facing the mother and the feet land under her arm. To be more comfortable, you can press a pillow under your arm.
The position armpit position is praised by moms who have been gifted by nature with big breasts, c-section women and ladies who suffer from breast inflammation and stagnant food.
When to breastfeed? How will I know when to stop?
How long should a woman breastfeed her baby? Views in this matter are divided. Different opinions are made by both doctors and specialists, as well as mothers with their own experiences. The most important guideline, however, is the opinion of the World Health Organization (WHO), which suggests that children should only be fed with breast milk until the sixth month of their life. We do not use alternatives other than women's milk, because it contains all the nutritional values and antibodies necessary for proper development of the baby. When the baby is over six months old, additional use of other food sources is recommended. This way - by natural feeding and other food products - the child can be fed up to three years of age. Most moms stop breastfeeding two-year-old children or younger, yet this is a very individual case.
Everything depends on the approach and predisposition of the young mother. Breastfeeding is a unique act of intimacy that creates a special bond between a woman and her child, and as such, it is of great importance for the further development of the toddler. It is a process based on mutual benefit that satisfies the need for proximity and security. Everything is based on the mother's wishes - if she feels she still wants and can breastfeed, there is nothing to stop her from holding her baby by her breast for as long as she wants. It is a myth that the baby will never give up breastfeeding on it's own, as many children over the age of three give clear signals that they no longer need this kind of nutrition. This is not always a simple, verbal message. Sometimes we need to look more closely at the behavior of our toddler. If a child becomes anxious and whiny at the feeding time, if it reacts nervously at the sight of a breast and hesitates whether it wants to use it at all, it is time to let it eat normal food.
Long-term breastfeeding must also be done with the full consent of the mother. If she has doubts, she is tired or discouraged, the child will certainly feel it, and shared meals will turn into unpleasant and nervous experiences. Forcing to feed always negatively affects both the woman and her baby. Each mother has the ability to choose and listen to one's own intuition. The good advice of "know-it-all" aunts and grandmothers will be of no avail, since every mother-child relationship is unique and special - and there should be absolutely no attempts to externally influence it. When breast-feeding comes with the freedom of choice, it will remain magical forever, worth remembering, a time of extraordinary closeness between the mother and her baby.
Breastfeeding after a caesarean. How to properly feed the baby after a c-section?
You probably heard many times that women after a c-section are unable to breastfeed their baby because there is no milk in their breasts. This is an obvious myth - for the record, maternal milk production begins with the 16th week of pregnancy. The biggest signal for the hormone responsible for the production of milk, that is, prolactin, is sent to the brain when the placenta is removed from the uterus. This process takes place in case of both surgical and natural labor, hence the belief that the c-section prevents breastfeeding finds no confirmation in the actual state of affairs.
Anyway, it may cause some problems, though. Their source is the lack of contact between the mother and her baby shortly after birth. C-section is usually performed with use of general anesthesia, which lasts for a long time. The extremely important, first hour after childbirth, mom and the child spend separately, which significantly affects the little man's reflexes when it comes to latching to the breast. Sometimes, it is also the case that the staff decides on artificial feeding of the baby and then the child is difficult to get re-accustomed to the breast. However, there are no problems that can't be solved through patience and consistency.
Nowadays hospitals are increasingly using the so-called "wire line anesthesia" that allows patients to remain fully awake during surgery. Thanks to this type of anesthesia the baby can be given to it's immediately after birth - and as a result, can be fed right away. You must remember to indicate to the hospital staff that during the surgery you only want to take medicines that will not harm your baby while breastfeeding. Don't be afraid to ask for help during the first feeding - midwives and nurses will certainly make it easier for your baby to feed so as not to irritate the wound on your belly.
If the newborn does not have a sucking reflex, do not be discouraged. Patiently latch it to your breast for every feeding, even if it is sleepy and does not want to cooperate fully. Do not try to use a breast pump - mothers and babies are so correlated that systematic breast feeding will help to regulate the lactation. Most important are the desire and a bit of stubbornness.
Breastfeeding problems. How to cope with lack of food? What is breast fullness?
Most women on their way to comfortable and satisfying breastfeeding may encounter many problems that can turn a baby's diet into a real battle. Women complain of painfully bitten breasts, increased or stopped lactation, or baby's problems with proper suction. Sometimes a toddler likes a particular breast and refuses to latch on the other. Some women also have inflammation and swelling of the milk glands, which significantly affects their daily comfort and takes away any signs of pleasure. But there are methods and solutions to everything, and many things just need patience and systematicity. Here are the most common problems with breastfeeding:
No breast milk
Hungry baby sucks the breast, and there's hardly any milk inside? Do you want to cry, because the only thing you can do is to reach for a bottle and feed the baby with artificially modified food? Do not break and do not give up! The basic method for stimulating lactation is frequent placement of the baby to the breast. The longer and longer you stimulate the glands by feeding the baby, the greater chance that the milk will finally appear. Spend a lot of time lying down, hugging your toddler and giving it the access to your breast. When sucked, the nerve endings of the nipple send a signal to the pituitary gland responsible for producing the hormones responsible for the production of food - prolactin and oxytocin.
Breast pumps may also be of great value. They are the devices used to extract breast milk. On the market there are various variants and types - manual, electric, equipped with massage pads and those that mimic the breast sucking process. To effectively stimulate your breasts to release milk, you should use breast pumps after each successful baby feeding.
Breast fullness - how to cope with the food mess in the first days of breastfeeding?
The breast fullness is a physiological state in which, after about 40 hours from labour, too much milk appears. Usually it is a harbinger of successful lactation, however, it is not a comfortable condition for the mother. The breasts become swollen and tense and the milk fills them in excess, often spontaneously spilling from the nipples. Its production increases from 100 ml produced 24 hours after delivery to 750 ml on the fourth day. Breast fullness passes with time, but you should make sure that the baby successively emptied the breast from the food. If your breasts are not sucked regularly, you may overfill the lactiferous ducts and that leads directly to breast inflammation. To reduce the amount of food, it is best to have your baby feed as often as possible (up to 14 times a day, including the night). It is important for the baby to latch properly to the breast. Just before feeding, you can pull off some milk, which will soften the nipples and make it easier for your baby to suck. Cold compresses of wet fabrics or cabbage leaves bring relief to sore breasts.
Nursing a newborn - how to prepare?
To prepare for this extremely important stage in each mom's life, remember that we will do nothing better than mother nature herself. And although it was once recommended that young mothers prepare their breasts using proper training before feeding time, it is now believed that our body is able to prepare itself for this fascinating process. Therefore, any tips saying that every mom should prepare the nipples by rubbing them with a rough towel and olive oil, are nothing more than fat fish tales. Same with the belief that from the 8th month of pregnancy she should daily lubricate on them a bit of colostrum (so called first milk, a mixture of protein, antibodies, vitamin A, chlorides and sodium, which are crucial for the development of digestive and immune systems in a newborn). All these treatments were intended to strengthen and elasticize the skin of the nipples and to be a form of prevention against inflammations of the mammary glands. Today's professionals are unanimous - the process of successful and undisturbed breastfeeding does not depend on previous preparation. It is regulated rather systematically and correctly by latching the baby and learning the correct suction. So instead of focusing on what you hear through the grapevine, it's better to start with proper feeding habits both for you and your baby.
Cigarette smoking and breast-feeding
Nursing mothers and pregnant women should give up smoking as soon as they realize that a new family member will be born into their lives. This also applies to chewing tobacco, nicotine gum, snuff and even, popular in recent years, E-cigarettes . Tar and nicotine substances easily get into the breast milk and can cause irreparable damage to your baby's body. Moreover, the concentration of nicotine in the blood of a smoker is much smaller than the amount that accumulates in the milk. This means that while smoking and breastfeeding, we provide the child with bigger amount of toxic substances than we have impacting our own body.
The negative effects of smoking while breastfeeding include:
- Reduced milk production - Breasts of s smoker often contain much less milk than those of non-smokers. This means that the baby will no longer receive the food portions necessary for its proper development. The reason for this is nicotine, which has properties that impair the production of prolactin - the hormone responsible for lactation.
- The drop in milk quality - the milk of smokers is 19% less fat than the mothers who completely quit smoking. This has a huge impact on normal development processes of the newborn - the child may have lower body weight and reduced neuro-developmental skills.
- Reduction of vitamins - the milk of smokers has a lower content of vitamins A, E and D3, which are extremely important antioxidants.
- Frequent colic - according to research, children fed by smokers may have painful colic twice as often as the ones fed by non-smokers. Probable cause of this condition is the impact that nicotine has on increasing intestinal protein concentration. Their hyperactivity can cause the occurrence of nagging cramps commonly known as "colic." This may be related to the tendency that children of smokers cry more often than their, fed by no-nicotine milk, colleagues .
- The risk of damage to the central nervous system - smoking significantly impairs the processes involved in transporting iodine to breast milk. This extremely important macroelement is crucial for the development of the internal organs of the baby's body. Therefore, iodine deficiencies can manifest themselves in the form of damage to the nervous system (CNS), disorders in the development of the child's skeleton and problems with the thyroid gland.
- Increased risk of oxidative stress syndrome - children that have prolonged exposure to tobacco smoke are in direct danger of oxidative stress. This is a state in which the body's natural oxygen balance is disturbed. This is due to excessive production of free radicals or a decrease in antioxidant activity. It has been proven that tobacco smoke is one of the major sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS), that is, free radicals responsible for aging processes. These species force the body to produce an antioxidant barrier, which causes a disturbance in the body's oxygen balance. Negative influence of free radicals causes a number of side effects in the form of chromosomal cracks or point mutations. Oxidative stress can also be associated with pre-existing conditions such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia or necrotizing enterocolitis.
- Reduced efficiency of antibodies contained in breast milk - The immune system of a breastfed infant does not develop properly as the antibodies delivered to it lose their protective properties under the influence of nicotine and other harmful substances.
- Shortened lactation time - smoking pregnant mothers point out that frequent smoking of tobacco products significantly shortens their total lactation time.
- Excitation of the baby, frequent crying, problems falling asleep - children who, along with their mother's milk, also consume nicotine and other substances from cigarettes often suffer from their stimulant effects. This can affect the baby's daily functioning, it's tendency to cry frequently, and sleep problems. The child is whiny and tired, but it still wriggles and does not want to go to sleep.
- Changing the taste of milk - Tobacco can significantly affect the taste of milk, which can lead to problems with the baby.

What if we can not stop smoking during lactation? Do cigarettes mean termination of breastfeeding?
Specialist physicians have long debated on the impact of cigarettes on the health of a breast-fed child in opposition to smoking at artificially fed babies. The verdict was unambiguously clear: if a mother is unable to give up smoking, she should not stop feeding. Artificial feeding combined with passive smoking causes more adverse health problems for the toddler than it would for natural feeding during cigarette smoking.
In other words - if you smoke, do not give up breastfeeding! You should always do exactly the opposite, that is, at the time of feeding completely reject the stimulant. However, if you are unable to do so, try to at least apply some rules that will help minimize the harmful impact of smoking on your baby's development. Here they are:
- Reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke. Best to zero;
- Plan the time of smoking so as to maximize the time between cigarette and baby feeding. Studies indicate that 95 minutes after cigarette smoking the nicotine content in the mother's blood drops by at least half;
- Do not smoke tobacco in the presence of the child and prevent such behavior among other household members;
- Do not smoke in the room where the child is staying - his room, a common bedroom, the kitchen, the car;
- After smoking a cigarette, change clothes and wash hands thoroughly. Only then can you touch and deal with your baby;
- Also watch out for E-cigarettes - their exact effect on maternal milk has not yet been thoroughly investigated.
Contraception and breastfeeding
You have successfully completed your pregnancy and now you are breastfeeding. You know you do not want to give your younger sibling a baby now, so there's a very important issue on the horizon. What kind of contraceptives can a nursing mother use? Which of them are completely safe for the developing of your baby's body, which should be abandoned unconditionally, and how many truths lie in the statement that breastfeeding itself is an effective type of contraception?
Breastfeeding infertility
Starting from the end - you probably heard many times that if you are breastfeeding you do not need to be protected against pregnancy. It would be a very comfortable and economical solution, but don't get excited quite yet. For breastfeeding to actually act as a kind of contraception (or so-called breast-feeding infertility) the following conditions must be met:
- Your child must be fed only by natural means. It is excluded of feeding - even sporadically - with any artificial mixture. You can not give your child water or tea.
- The baby must be fed on demand - both during the day and at night
- The child must be fed regularly and without breaks longer than six hours
- You have to breastfeed for at least 100 minutes a day
- The baby should not use a teat, as it may adversely affect latching to the breast
- It is forbidden to take any medication - the mother must be completely healthy
- There will still occur the puerperal lack of monthly bleeding
It is really easy to break even one of these conditions, which usually results in a lack of guarantee of contraception. Infertility in lactation is associated with the active action of prolactin - a hormone that stops the ovulation process. Doctors estimate that the credible duration of lactating infertility persists until about three months old. And then you definitely have to give up this rigorous method when your child completes the sixth month. Then the mother's milk should be gradually replaced by solid foods.
Contraception prohibited when breastfeeding
During lactation, you can't use hormonal contraception, which is based on estrogen. This hormone is found in most commercially available two-pack contraceptives (estrogen-progesterone). It has been proven that estrogen-based drugs partially stop lactation, leading to the need for artificial feeding and may result in premature withdrawal of the breast. The sooner after giving birth to a two-component contraceptive based estrogen, the greater the effect of drugs on reducing lactation. In addition, estrogen can alter the mixture of maternal milk, which adversely affects the health of the toddler.
Contraceptives allowed during breastfeeding
There are quite many contraceptive methods, that poses no threat to lactation. Every mom can choose from a variety of methods - both mechanical and hormonal. Here are the most common contraceptives allowed during breast-feeding:
- Condoms
Mechanical contraceptives include condoms. Regardless of whether they are covered with spermicide, special humidifiers, or belong to standard models, condoms have no effect on lactation and can be used immediately after birth. - One-component birth control pills
Mini-pills containing progestagen are considered safe for lactation. Their contraceptive effect is based on the thickening of the cervical mucus and the reduction of the probability of ovulation. They should be used every day at the same time. - Hormone intramuscular injection
An injection that provides a systematic release of the hormone responsible for stopping the ovulation process. Thanks to the intramuscular delivery form, it bypasses the stomach and acts directly on the mucous membrane of the uterus. Safe for breastfeeding mothers, however, should only be used after six weeks of childbirth. - Hormone insemination insert
Intramammary insert, which purpose is the regular release of the progestogen - the hormone responsible for stopping ovulation. Its performance is evaluated 5 years after insertion. A nursing woman may undergo insertion surgery at 6 weeks postpartum. - Copper insemination insert
Usually made of copper, the intrauterine insert, which is based on spermicidal properties of copper ions and the development of sterile inflammation in the uterus. This condition prevents the embryo from nesting in the wall of the uterus. The insert can be used as early as the sixth week after birth. - The"after"pill
Contraceptive contraception, or pills used after unprotected sexual activity, is not attributed to negative effects on lactation. Some doctors, however, have indicated that they should stop feeding their baby up to 36 hours after taking a tablet based on ulipristal acetate. Furthermore, it should be borne in mind that as such an "after" pill can not be a substitute for regular contraception, and its use should only occur sporadically.
Keep in mind that every type of contraception you take during the lactation should be consulted with your gynecologist. A specialist will help you choose the pill appropriately, recommend the best intramuscular inserts, or suggest suitable alternatives. Do not choose drugs blindly, in the end we must also consider the good of our baby!
What else should you avoid while breastfeeding? Can you dye your hair and lie on a tanning bed during lactation?
Many young mothers wonder whether they should avoid the care treatments they used to undergo before and during pregnancy, such as the use of tanning beds or hair dyeing during lactation. Women often do not know whether it will have a negative impact on food, and thus on the child. Will a visit in a solarium affect the quality of food? And whether artificial substances contained in traditional hair dyes can get into their body, and from it through food also into the body of their baby? We are eager to answer!
Can the tanning bed negatively affect the natural breastfeeding process?
Solarium has no negative effect on the quality or composition of the food. Like tanning, it can cause burns to the skin of the breast and sensitive skin of the nipples, making feeding very painful and sometimes impossible. However, if we go to a solarium regularly and we know how our skin responds to this type of radiation, breastfeeding is not a clear reason to give up treatments. We can also cover breasts or at least nipples and protect them in this way from possible burns.
Remember, however, that this does not mean that solarium is a completely safe beauty treatment. Tests have already proven over a dozen years ago that exposing the skin to artificially generated UV radiation is just as harmful as staying in the sun for several hours without protecting it with suitable filters with high sun protection rates. Frequent sunbathing can cause the skin to age faster and lose its firmness. It was also found that the use of tanning beds significantly increases the risk of developing skin cancer, i.e. melanoma, which is one of the most dangerous and fastest developing cancers.

Dyeing hair banned during breastfeeding – a fact or myth?
The fact that women should not dye their hair during breastfeeding is obviously a myth. Unfortunately, it has existed in our society for several decades. It was feared then that the chemicals contained in the dyes can get into the woman's body through the scalp and penetrate into her food. Today we know that it is not true. Hair dyes have no effect on mother's milk, its composition, quality or taste. In addition, there are more and more products on the market that contain many natural substances, such as plant extracts and oils, thanks to which modern products work equally effectively, without destroying hair and posing no threat to the sensitive scalp.
However, it is also a matter of hair dyeing by women who are losing hair and have problems with hair weakness after childbirth. In such cases, it is worth investing in the most natural dyeing cosmetics, which will not only not deepen the bad condition of hair but will help them return to their pre-pregnancy state. First of all, we should avoid dyes produced on the basis of ammonia, which additionally dry the hair and increase their fragility. For some, a good choice would be even delicate coloring cosmetics, such as coloring shampoos. Their effect is maintained much shorter than the effect obtained with the help of traditional dyes. However, these cosmetics are much less aggravating for hair and can help us speed up their regeneration while providing a well-groomed look and dealing with the most unruly baby hair.
Can we continue to breastfeed during menstruation and pregnancy?
Other important questions asked by young mothers include breastfeeding during pregnancy and menstruation. Should we avoid breastfeeding or take any special precautions during menstruation? Will we still be able to breastfeed our first child if we get pregnant again soon after giving birth? How to deal with such cases?
Breastfeeding during menstruation
When breastfeeding a baby, we do not have to worry about our period for at least the first nine months of a child's life. In women who decide to breastfeed naturally during the day and at night, and do not use breast pumps or other devices, menstruation returns only after 9 to 18 months from delivery. It is also important not to use hormonal contraceptives and other substances that may affect the body's hormonal balance. In some cases, it happens that the period appears even after two years. It is completely natural and does not give any reason to worry.
In women who decide to breastfeed as well as using additional artificial blends, the period may appear as early as 2-3 months after delivery. It is influenced by the fact that even adding one meal other than breast milk significantly reduces the time and frequency of breast stimulation by the child. In some women also in this case menstruation may appear much later, even when the child completely switches to other foods.
But what if we get our period when breastfeeding? Should you avoid breastfeeding then? Absolutely not! It is true that during the period the taste of milk may change and its amount may seem to be reduced by the impeded flow caused by menstruation or associated swelling of our breasts. The breasts can also be tender and even sore, which may cause serious discomfort to some young mothers during breastfeeding. However, the composition and quality of milk does not change, which still contains all the nutrients needed by the child. On average, after the first three days of the period, the amount of milk returns to normal and the painfulness of the breasts disappears. Some children seem to need much more food then, which is only due to the difficulty of getting into it during the early days of menstruation. In order for problems related to lower milk production during the period to not be so burdensome for a small baby, it is worth choosing to introduce supplements containing calcium and magnesium into our diet. The use of food containing these elements from the middle of the cycle to the third day of the period will help us provide our baby with maximum comfort and allow us to effectively breastfeed even during menstruation.

Pregnancy and breastfeeding
There are surprisingly many controversies and opinions around this topic that we can even refer to as legends. Many of them are associated with the boundless faith of some women and - surprisingly! - doctors in lactation infertility. According to one theory, nature should ensure that we do not get pregnant throughout the entire feeding period. We know, however, that breastfeeding is not a reliable method of contraception, and therefore pregnancy does occur in nursing mothers. At the same time, going into another pregnancy does not have to involve immediate withdrawal of the previous child from the breast! In the case of a safe pregnancy in a healthy woman, there is absolutely no need to quickly untie a baby from the breast. We can successfully feed throughout pregnancy, and even later, after the birth of another family member. Nature took care of it so that there would be enough food for two, and even for three babies born at short intervals of time. During pregnancy, however, the amount and taste of milk may change. The occurring hormonal changes cause similar effects as in the case of the occurrence of the period. However, the milk will still be of adequate quality and will provide the child with all the required nutrients.
Remember that the decision to feed your baby during the next pregnancy should depend primarily on the health and well-being of the woman. Some young moms may feel just too tired or too sore due to pregnancy, and initial nausea or later appearing back pains will cause them great discomfort associated with breastfeeding. Nursing a child may also be affected by significant breast pains associated with pregnancy. From a medical point of view, the decision to continue breastfeeding should be consulted with a physician in the event of severe contractions, bleeding or spotting, as well as pregnancy risk due to abnormalities in the placenta, shortened cervix and the history of previous miscarriages for unknown reasons. Then, it is necessary to take care not only of the health of the first child, but also take into account the safety of the mother and the developing fetus in her womb.